What is the valency of common academic verbs?

This is the third and final chapter about Verb Transitivity. To complete this reader, read each chapter carefully and then unlock and complete our materials to check your understanding.
– Introduce the most common 150 academic verbs
– Separate each verb into its valency groups, whether intransitive, monotransitive, ditransitive or tritransitive
– Provide examples in academic contexts for each valency type
Before you begin reading...
-
video and audio texts
-
knowledge checks and quizzes
-
skills practices, tasks and assignments
Chapter 3
This third and final chapter in our short reader on verb transitivity deals with determining the valency of the most common academic verbs so that students can use these verbs within their own academic presentations and essays. Remembering back to Chapters 1 and 2, valency (also known as transitivity) is the determination of how many arguments a verb grammatically requires. Such arguments may be subjects, direct objects, indirect objects and oblique objects. Because not all verbs are able to take objects, and those that can may be limited to the type and number of objects they take, it’s important that we group these verbs into their four valency categories so that they can be more easily and accurately used by learners of the English language.
What are the 150 most common verbs?
accept, achieve, adapt, advance, affect, allocate, allow, alter, analyse, appear, argue, arise, assert, assess, associate, assist, assume, attempt, avoid, base, benefit, cause, choose, cite, claim, clarify, classify, combine, compare, compete, concentrate, conclude, conduct, connect, consider, consist, constitute, construct, contrast, contribute, correspond, decline, define, demonstrate, depend, describe, design, determine, develop, differ, discuss, display, distinguish, effect, eliminate, emerge, enable, encounter, encourage, enhance, ensure, evaluate, evolve, examine, exceed, exemplify, expand, explain, express, facilitate, favour, focus, form, formulate, function, generate, highlight, identify, illustrate, imply, improve, include, increase, indicate, influence, interpret, introduce, investigate, involve, isolate, lead, limit, locate, maintain, measure, neglect, note, obtain, occur, outline, overcome, participate, perceive, possess, predict, present, prevent, produce, prove, provide, publish, pursue, quote, receive, reduce, reflect, regard, reinforce, relate, remain, remove, replace, report, represent, reproduce, resolve, respond, restrict, result, retain, reveal, select, separate, show, solve, specify, state, strengthen, stress, study, submit, suggest, summarise, support, tend, transform, treat, undermine, undertake, vary
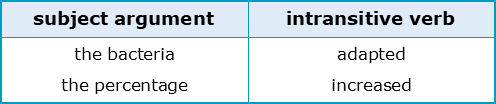
Which academic verbs are intransitive?
adapt, advance, appear, argue, choose, compete, concentrate, contribute, evolve, focus, function, increase, occur, participate, reflect, remain, result, strengthen, tend
“The bacteria quickly adapted (to its new environment).”
“The results did indeed develop (as predicted).”
“Something unusual emerged (from the results).”
“It increased (at a phenomenal rate).”
“All researchers should participate.”
With only 15/150 verbs being intransitive, this is not a common verb type in academic writing. The usual structure for intransitives has been included in the diagram below for your reference. Don’t forget, however, that optional adjuncts such as ‘quickly’ or ‘quicker than expected’ may also be included:
Which academic verbs are monotransitive?
accept, achieve, adapt, advance, affect, allocate, allow, alter, analyse, arise, assert, assess, associate, assist, assume, attempt, avoid, base, benefit, cause, choose, cite, claim, clarify, classify, combine, compare, concentrate, conclude, conduct, connect, consider, consist, constitute, construct, contrast, correspond, decline, define, demonstrate, depend, describe, design, determine, develop, differ, discuss, display, distinguish, effect, eliminate, emerge, enable, encounter, encourage, enhance, ensure, evaluate, examine, exceed, exemplify, expand, explain, express, facilitate, favour, form, formulate, generate, highlight, identify, illustrate, imply, improve, include, increase, indicate, influence, interpret, introduce, investigate, involve, isolate, lead, limit, locate, maintain, measure, neglect, note, obtain, outline, overcome, perceive, possess, predict, present, prevent, produce, prove, provide, publish, pursue, quote, receive, reduce, reflect, regard, reinforce, relate, remove, replace, report, represent, reproduce, resolve, respond, restrict, retain, reveal, select, separate, show, solve, specify, state, strengthen, stress, study, submit, suggest, summarise, support, tend, transform, treat, undermine, undertake, vary
“The board allocated $3,000 to the study.”
“The results benefited group A more than group B.”
“The scientists developed the vaccine over the course of three years.”
“I identified the problem with the methodology and rescheduled the test.”
“The experiment involved 2,500 participants from fifty-six countries around the world.”
With 142/150 verbs being monotransitive, this verb type is extremely common in academic contexts. The usual structure for monotransitives is included in the diagram below for your reference:

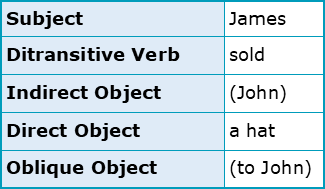
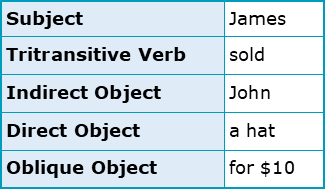
Which academic verbs are di/tritransitive?
allocate, allow, cause, design, present, provide, show
“The teacher allocated the students their homework.”
“The scientist allowed them the results.”
“She designed them the prototype they asked for.”
“The results provided him the answers he needed.”
“The results showed her the likely answer to her thesis.”
With only 7/150 verbs being ditransitive or tritransitive, this verb type is very uncommon in academic contexts such as presentations and essays. Ditransitive verbs are able to take subject, direct object and either indirect or oblique object arguments, while tritransitive verbs will include all four of these arguments. The usual structure for verbs such as these has been included in the diagram below for the reference of teachers and students:
Good work on completing this short reader on verb transitivity. Consider next studying Academic Marker’s other readers on syntax, and don’t forget to complete our beginner, intermediate and advanced worksheets on this topic to check your understanding.
Downloadables
Once you’ve completed all three chapters about verb transitivity, you might also wish to download our beginner, intermediate and advanced worksheets to test your progress or print for your students. These professional PDF worksheets can be easily accessed for only a few Academic Marks.
Collect Academic Marks
-
100 Marks for joining
-
25 Marks for daily e-learning
-
100-200 for feedback/testimonials
-
100-500 for referring your colleages/friends