What are 8 tips for summarising body arguments?

This is the second and final chapter about the Summary of Main Ideas. To complete this reader, read each chapter carefully and then unlock and complete our materials to check your understanding.
– Introduce eight tips for writing effective summaries in the concluding paragraph of an essay
– Use authentic examples to see the summary in context
– Encourage the completion of activities to improve English proficiency and to check progress and understanding
Before you begin reading...
-
video and audio texts
-
knowledge checks and quizzes
-
skills practices, tasks and assignments
Chapter 2
Having introduced the basics of the summary of main ideas element and described its purpose, location and length in a concluding paragraph, the second and final chapter of this short reader explores eight tips that make for effective writing. When reading the following tips, remember that this summary is where the writer reminds the reader of (a) the key arguments from the body section of their essay and (b) how the overall thesis has been investigated. If you wish to see your grades improve in this aspect of essay writing, follow the eight pointers below carefully.

Tip 1: Maintain the Body Section Order
Part of the process of making a logical essay is maintaining a logical order. You’ll no doubt spend a lot of time deciding the order of your main ideas in your body section so that they tackle the overall argument in the clearest way, so make sure you maintain that order in the outline of your thesis statement and in your concluding summary of ideas too. Reorganise that order in the final paragraph and you run the risk of confusing your reader and damaging the coherence of your essay.
Tip 2: Select the Key Supporting Details
As was mentioned in Chapter 1, you’ll not only wish to summarise the main ideas of your body paragraphs, but you should also consider including some of the key supporting details that explored those ideas too. The following summary excerpt has been taken from an example essay about the advantages and disadvantages of global warming. In addition to including the main idea of the first body paragraph, this sentence also refers to one of its supporting details:
“It has been shown that global warming can in fact have a potentially positive impact on the environment, with regions such as Siberia demonstrating increased floral fertility.”
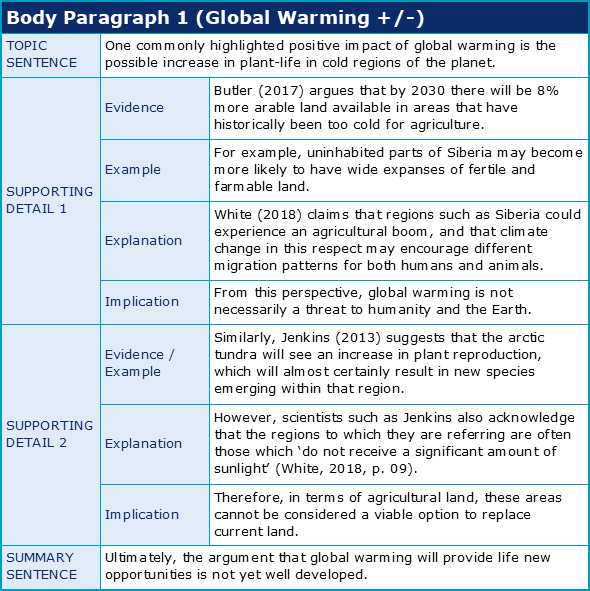
As can be seen when comparing the previous summary with this paragraph, only the most salient supporting detail has been selected. It’s important that a summary of main ideas is brief, so do be cautious with how many supporting details you add.
Tip 3: Avoid New Information
One tip that applies to every concluding element is that writers should avoid including new information. The conclusion is a place to review the arguments of the body section, not to include new sources, evidence, examples or explanation. You will not have time to explore new claims in detail, nor the word count to spare.
Tip 4: Tie the Ideas Together
An effective summary should also be tied together both in theme and through the cohesive devices that help signpost it. In the following example (taken from an essay about online language learning), the writer has achieved this togetherness (1) by using words such as ‘firstly’, ‘next’ and ‘finally’, (2) by making sure that all their main ideas explore the same topic, and (3) by ordering these ideas in the same way as presented in the body section:

Tip 5: Use Paraphrasing Techniques
Paraphrasing is a key part of the summary process. It’s not enough to simply repeat the main ideas from the body, a good writer should rewrite these ideas in different words that manage to maintain the same meaning. From the reader’s perspective, it’s much easier to absorb the same concept if you’ve read about it in more than one way. To paraphrase the main ideas successfully, below are some common techniques students can use:
- alter the grammar
- alter the sentence structure
- change the word order
- modify the word forms
- use antonyms and synonyms

Tip 6: Use Summarising Techniques
Of course, there’s a little more to summarising than just paraphrasing. An effective academic summary should also:
- be brief and concise
- be neutral and informative
- be selective of the information included
- maintain the meaning of the original
- synthesise numerous ideas into one section
Tip 7: Be Concise and Specific
Next is being concise and specific. Why say the same thing in more words if you can say it in fewer? Why be vague about your ideas unless you’re unsure about them? The less effort is needed for your reader to be reminded of your main ideas and supporting details the better. Take a look at the following two summaries and decide which has the best balance of concision and specificity:
i) Firstly, the increase of a language learner’s vocabulary was explored, finding that online learning was more conducive to autonomous learning. This autonomy has a direct tendency to encourage vocabulary growth. Next, a student’s ‘willingness to communicate’ was discussed, and was found to be much the same in European contexts whether a student participated in online or offline classes. Finally, speaker confidence, an important aspect of language learning, was shown to improve in some cases, much to the surprise of researchers in the field.
ii) In the first main idea, the large increase in a language learner’s ability was explored in lots of detail, finding that learning in an online setting was more conducive to learning in an independent way. This independent learning has a direct tendency to encourage growth of certain aspects such as vocabulary. Next, an undergraduate student’s ‘willingness to communicate’ was discussed in many sentences, and was found to be much the same in European contexts such as Italy and Spain and Germany whether a student participated in classes or not. Finally, the confidence of a speaker, which is an important aspect of learning a language such as English and Spanish, was shown to improve in some cases, much to the surprise of some people who work in the field of linguistics and the English language.

Tip 8: Edit and Proofread Carefully
Finally, never forget to edit and proofread every element of your essay for grammatical accuracy, typos and spelling mistakes. A submission that’s free of simple errors such as these is much more likely to impress a reader or university assessor. It would be shame after all your hard work in researching, planning and drafting your essay to lose out on valuable marks simply because you missed a few commas or used the wrong tense.
To reference this reader:
Academic Marker (2022) Summary of Main Ideas. Available at: https://academicmarker.com/essay-writing/concluding-paragraphs/summary-of-main-ideas/ (Accessed: Date Month Year).
Downloadables
Once you’ve completed both chapters in this short reader about Summary of Main Ideas, you might then wish to download our Chapter Worksheets to check your progress or print for your students. These professional PDF worksheets can be easily accessed for only a few Academic Marks.
Chapter 1 explores the topic: Why summarise the main ideas in a conclusion? Our Chapter 1 Worksheet (containing guidance, activities and answer keys) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
Chapter 2 explores the topic: What are 8 tips for summarising body arguments? Our Chapter 2 Worksheet (containing guidance, activities and answer keys) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
To save yourself 1 Marks, click on the button below to gain unlimited access to all of our Summary of Main Ideas Chapter Worksheets. This All-in-1 Pack includes every chapter, activity and answer key related this topic in one handy and professional PDF.
Collect Academic Marks
-
100 Marks for joining
-
25 Marks for daily e-learning
-
100-200 for feedback/testimonials
-
100-500 for referring your colleages/friends