What are the seven unique functions of full stops?

This is the second of three chapter about Full Stops. To complete this reader, read each chapters carefully and then unlock and complete our materials to check your understanding.
– Explore the concept of how punctuation marks have functions
– Detail the seven unique functions of full stops
– Provide examples of each function to help guide the reader
Chapter 2
This second chapter about full stops (periods, in American English) focuses on the seven common functions of this punctuation mark in the English language, as were briefly outlined in Chapter 1. Each of these functions will be explained and exemplified in turn. By learning exactly how and when to use full stops when writing, students will likely increase their chances of submitting a well-edited assignment that better guarantees clarity, accuracy and academic success.
Function 1: Finishing Declarative Sentences
The first function of full stops is that they can be used to mark the end of a declarative sentence. Declaratives, which are one of the four sentence functions in English, are those sentences that provide the reader with an idea or statement that may be either objective/subjective and true/false. As can be seen in the following examples, what separates the declarative from interrogatives, imperatives and exclamatives is that this sentence type is always finished with a clear full stop:
Examples:
– One example of this can be found in the Warsaw Pact.
– My university has over 10,000 students and 600 tutors.
– Smith (2016) suggests that student attendance is improving every year.
– Blended Learning is defined as the process of teaching and learning online.
– Because it’s so important, students need to focus in foundation-year programmes.
If a writer were to decide not to use a full stop in sentences such as these, it would become very unclear for the reader where one sentence begins and another finishes.
Function 2: Finishing Imperative Sentences
Full stops can also be helpful in indicating the end of an imperative sentence, which is another of the four sentence functions. However, depending on the strength of the proposition and the writer’s preference, imperatives (unlike declaratives) may take either a full stop or an exclamation mark (!). As is shown in the following examples, imperatives are the commands, requests, instructions or directions that are aimed at a listener or reader, and which are far more commonly used in general than academic English:
Examples:
– Turn to page 53.
– Turn right at the library.
– No talking during the exam!
– Discuss these three questions with your partner.
– Leave your bags and coats at the front of the room.
Function 3: Finishing Indirect Questions
Much like for declaratives and imperatives, indirect questions are also usually completed with a full stop. Indirect questions do not normally follow the same grammar as direct questions (interrogatives) which are always completed with a question mark, and are instead more similar to declarative statements that contain a questioning element such as ‘why’ or ‘how’. For clarity, some academic examples are provided for you below:
Examples:
– I wonder where they are.
– They really have no clue how to study.
– I don’t know whether you will fail or not.
– I hope the students know when the exam starts.
– The teacher asked me why my assignment was late.
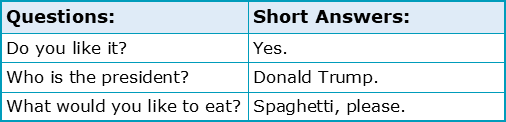
Function 4: Providing Short Answers:
Full stops are also useful for providing short answers to yes/no and closed questions, which may even be so short as to contain only one word:
Function 5: Abbreviating
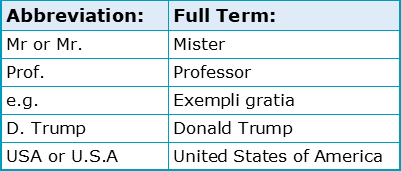
The fifth function of full stops becomes apparent when abbreviating. An abbreviation is when either a word, phrase or longer piece of text has been reduced in length by a speaker or writer. While there are many types of abbreviations such as acronyms, contractions and initialisms, it’s important to note that full stops are only necessary with certain abbreviation types. Although some examples are provided below, more detail will be provided in Chapter 3:
Function 6: Computing
In computing, the full stop (called a ‘dot’ or a ‘full point’) can also be very useful. As can be seen in the following examples, this punctuation mark may be used as a delimiter in DNS lookups (IP addresses), in file names, and in web addresses:
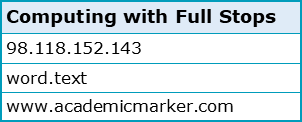
In truth, without including the full stop in the these examples, items such as these would not open or function correctly. The IP address would be incorrect, the document corrupted, and the web address unfound.
Function 7: Counting
The final function of full stops is to separate one number from another. This could be to indicate a part or fraction of a whole number, when showing the number of cents within a dollar, or when telling the time (in British English, at least):

Downloadables
Once you’ve completed all three chapters about full stops, you might also wish to download our beginner, intermediate and advanced worksheets to test your progress or print for your students. These professional PDF worksheets can be easily accessed for only a few Academic Marks.
Collect Academic Marks
-
100 Marks for joining
-
25 Marks for daily e-learning
-
100-200 for feedback/testimonials
-
100-500 for referring your colleages/friends