What are the key facts about bachelor’s degrees?

This is the first of three chapters about Bachelor’s Degrees. To complete this reader, read each chapter carefully and then unlock and complete our materials to check your understanding.
– Introduce the concept of university bachelor’s degrees
– Explore the different types of bachelor’s degree
– Consider the benefits and costs of bachelor’s degrees
Chapter 1
In recent years, a level of education that was once reserved for the wealthy or highly intelligent has become almost normal in many cultures around the world, with students often leaving high school and entering unquestionably into costly university degrees. Although for many this direction is quite expected, few students ever take the opportunity to consider what a bachelor’s degree is and what to expect while studying one. In this short three-chapter reader on the topic, Chapter 1 aims to first give an overview of undergraduate programmes before Chapter 2 then offers guidance about selecting the most appropriate major. Finally, Chapter 3 provides ten tips about how to succeed and make the most of this valuable learning experience.

What is a Bachelor’s Degree?
A bachelor’s degree is typically a three- to four-year full-time programme of study that leads to recognised qualifications which are awarded by universities and colleges and which contribute to career development. Though the majority of courses are conducted on campus, it is now possible to complete a bachelor’s programme either part-time or online provided you have the time and money – and a stable internet connection.
While bachelor’s degrees can be completed by any capable person of any age, the most common age of enrolment for a first degree (also known as an undergraduate degree) is around eighteen. Entrance into such programmes is usually following the successful completion of a standardised set of university-entrance examinations – such as the SATs in the US, A-levels in the UK, or the Gaokao in China. For part-time and distance programmes however, there has in recent years been an increasing market of mature students who may enrol onto bachelor’s degrees through alternative access programmes.
The general purpose of a bachelor’s degree is to educate students in a specific discipline to a level of expertise that will prepare them for the working world, while also honing skills in writing, research, presentation and critical thinking. Of course, the knowledge that is specifically learned and practiced varies from subject to subject and from institution to institution, which is why it’s important for students to carefully consider the degree major and university they choose.
Are there different bachelor’s degrees?
Although not complete, what can be seen from the following table is that there are many different types of bachelor’s degree available to students depending on the discipline and area of study:
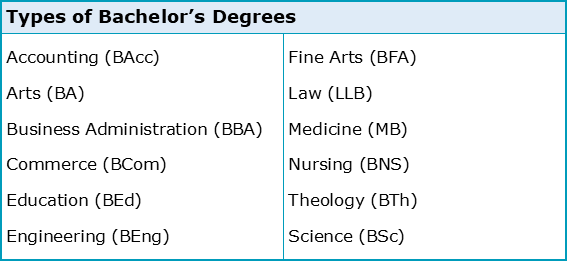
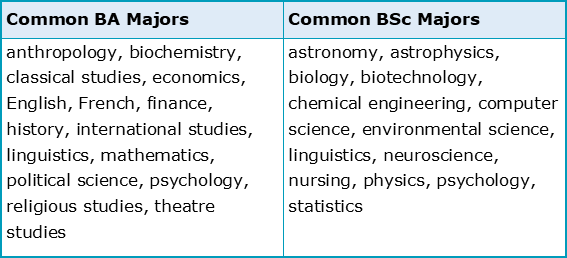
While there’s certainly a lot of variety here, the two most common types are the Bachelor of Arts (BA) and Bachelor of Science (BSc) qualifications. This is because most of the disciplines previously exemplified are commonly grouped under either the arts or the sciences instead of being uniquely identified. However, as the next table hopes to clarify, it’s not always obvious as to which major falls under the arts and which the sciences, and in truth subjects such as linguistics or psychology may vary between the two depending on the modules involved:
Another factor to be aware of when understanding bachelor’s degrees is that the type of degree you enrol onto will likely shape the type of assignments you will complete and the extra components that may be on offer, such as internships or opportunities to study abroad. Universities are also heavily influenced by the education culture of their country, creating differences in how the content is taught, how seminars and lectures are conducted, how many students are in each class, the quality of the resources, and the length of the semesters.
Are bachelor’s degrees essential?
The usefulness of a bachelor’s degree is quite dependent on your country of residence, your career level and the talents you’ve already developed. If you have a clear idea of the job path you’d like to follow for example, and know that it doesn’t really require a degree certification, then doing one would perhaps not be worth the time or expense. In Europe, less than half of all high-school graduates enter directly into a university programme, suggesting that culturally and economically there are career paths that do not require tertiary qualifications. In contrast, countries such as South Korea have reported that as many as nine out of ten secondary-school graduates continue on to university. Regardless of perceived necessity, we’ve provided below four clear benefits of having a bachelor’s degree:
Benefit 1: Career Choices
Having a degree will likely keep your options open. In truth, in several sectors such as education, science, and technology, many entry-level jobs already request degree holders. Bachelor’s degrees can also be useful stepping stones for continuing education, with students becoming even more specialised and expert in a subject by taking master’s degrees that increase competitiveness in the job market.
Benefit 2: Personal Development
Degrees can also equip students with lifelong skills of self-reflection, self-development, professional presentation, teamwork and critical analysis. Through continued assessments, critical feedback and exposure to different students from diverse backgrounds, degrees facilitate adaptability and open-mindedness.
Benefit 3: Networking Opportunities
No matter the subject, bachelor’s degrees also offer the opportunity to meet experts in the field, providing insight into careers that may otherwise be difficult to obtain. Students will also likely build relationships with staff that may prove to become excellent educational and professional contacts in the future, and may additionally establish in-group ties through the joining of campus societies – which in some cultures is almost as important as the degree itself.
Benefit 4: Increased Salary
Finally, degree-holding citizens are usually found to earn more across their lifetime than those who do not continue on to tertiary education. Whether or not this offsets the high costs of many degrees today is another matter worth discussing.
Are bachelor’s degrees expensive?
When deciding the usefulness of a degree, it’s important to consider whether the benefits of doing one outweigh the costs incurred. The cost of a bachelor’s degree is of course highly dependent on the country of study and whether you are deemed a national or international student. In the UK, for example, the cost of a degree is an almost equitable GBP9,000 per year at all universities regardless of reputation and ranking, whereas in the USA this number can vary greatly depending on the type of institute and whether you’re studying in or out of state. Many European countries still charge very little for their undergraduate programmes, and some are even free.
When deciding how useful a degree is versus cost, it may therefore be worth asking yourself (1) how many years long is the degree, (2) how much is tuition per year, (3) are there additional fees for books or other resources, (4) how high are the accommodation costs, (5) are there any scholarships available that you are eligible for, and (6) what loans are available to support your studies? Ultimately, the only person who can decide the value of a degree is you, but it would certainly be worth speaking with your family and peers to get their advice on the matter.
Now that you’ve completed an overview of what bachelor’s degrees are and to what extent one may be useful, Chapter 2 offers guidance on how students can select the most appropriate degree programme for their interests and career prospects. Before reading on however, you may wish to first review the information presented here by completing the activities in our Chapter 1 Worksheet.
To reference this reader:
Academic Marker (2022) Bachelor’s Degrees. Available at: https://academicmarker.com/careers-advice/getting-qualified/bachelors-degrees/ (Accessed: Date Month Year).
Downloadables
Once you’ve completed all three chapters in this short reader about Bachelor’s Degrees, you might then wish to download our Chapter Worksheets to check your progress or print for your students. These professional PDF worksheets can be easily accessed for only a few Academic Marks.
Chapter 1 explores the topic: What are the key facts about bachelor’s degrees? Our Chapter 1 Worksheet (containing guidance, activities and answer keys) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
Chapter 2 explores the topic: How can I best choose an undergraduate degree? Our Chapter 2 Worksheet (containing guidance, activities and answer keys) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
Chapter 3 explores the topic: What are 10 tips for bachelor’s degree success? Our Chapter 3 Worksheet (containing guidance, activities and answer keys) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
To save yourself 2 Marks, click on the button below to gain unlimited access to all of our Bachelor’s Degrees Chapter Worksheets. This All-in-1 Pack includes every chapter, activity and answer key related to this topic in one handy and professional PDF.
Collect Academic Marks
-
100 Marks for joining
-
25 Marks for daily e-learning
-
100-200 for feedback/testimonials
-
100-500 for referring your colleages/friends